What is Hyperlipidemia?
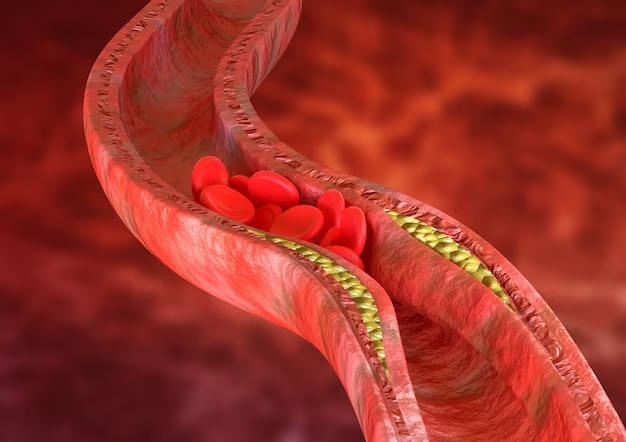
Hyperlipidemia, meaning can be described as a medical condition characterised by elevated levels of lipids, or fats, in the blood. These lipids, which include triglycerides and cholesterol, are necessary for healthy body function but can be harmful if they are in excess. Although hyperlipidemia frequently manifests without any obvious symptoms, it poses a serious risk for the emergence of cardiovascular conditions like atherosclerosis. Plaque accumulating inside arteries causes atherosclerosis, which increases the risk of a heart attack or stroke and restricts blood flow.
Genetics, dietary patterns, and way of life decisions are just a few of the variables that can play a role in the development of hyperlipidemia. The typical course of treatment entails dietary and lifestyle changes, along with exercise, and may also involve the use of medications to lower blood lipid levels. Controlling hyperlipidemia can help lower the risk of cardiovascular disease and enhance general health. It is crucial to consult your healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and course of treatment if you think you may have hyperlipidemia.
How serious is Hyperlipidemia?
Hyperlipidemia definition states that it is a medical condition characterised by elevated blood levels of lipids, such as cholesterol and triglycerides. Although the body needs lipids in some amounts for proper operation, excessive amounts can have negative effects on health.
- Health Effects of Hyperlipidemia: Atherosclerosis, which develops when plaque accumulates on artery walls and causes thickening and narrowing, can be brought on by high levels of lipids. Because of the condition’s limitations on blood flow to the organs, heart attacks and strokes are more likely to occur.
- Hyperlipidemia Risk Factors: Hyperlipidemia is frequently associated with other medical conditions such as hypertension and diabetes, which can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease even further.
- The Importance of Regular Monitoring: Regular lipid level monitoring is critical for the early detection and effective management of hyperlipidemia.
Hyperlipidemia is a serious condition that can lead to significant health complications if left untreated. It is crucial to work with a healthcare provider to manage lipid levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Signs and symptoms of Hyperlipidemia?
Hyperlipidemia is the medical condition that is also characterised by elevated levels of lipids in the blood and it is also known as high cholesterol. While some individuals with hyperlipidemia may not experience any symptoms, others may experience certain signs and symptoms that can indicate the condition.
Some signs and symptoms of hyperlipidemia include:
- Xanthomas: Xanthomas are fatty deposits that develop on the elbows, knees, hands, and feet due to high levels of lipids in the blood. They are often yellowish in colour and can vary in size.
- Xanthelasma: Xanthelasma, similar to xanthomas, are fatty deposits that can develop around the eyes, particularly on the upper eyelids.
- Chest Pain: Hyperlipidemia increases the risk of developing coronary artery disease, which can cause chest pain or angina due to high cholesterol.
- Shortness of Breath: In advanced cases of hyperlipidemia, the arteries may become so narrowed that they limit the amount of oxygen-rich blood reaching the lungs, leading to shortness of breath.
- Numbness or Tingling in the Extremities: High levels of lipids in the blood can also damage nerves, leading to numbness or tingling in the hands and feet.
Since hyperlipidemia can also manifest without any symptoms, routine blood tests are essential for both early detection and management.
What causes cholesterol to get high?
Hyperlipidemia, which is also known as High cholesterol, can be caused by a variety of factors. These factors include:
- Genetics: Genetics plays an important role in the development of Hyperlipidemia. Some people inherit genes that cause their bodies to produce more cholesterol than normal.
- Diet: Eating foods that are high in saturated and trans fats, as well as cholesterol, increases your cholesterol levels leading to hyperlipidemia.
- Weight: Being overweight or obese puts you at increased risk of having higher cholesterol
- Age and gender: As people age, their cholesterol levels tend to increase. Men are also at a higher risk of developing high cholesterol compared to women.
- Medical conditions: Medical conditions, such as diabetes, hypothyroidism, and liver or kidney disease, can also lead to high cholesterol.
It’s important to note that in many cases, high cholesterol does not cause any symptoms. Therefore, it’s important to have your cholesterol levels checked regularly by a healthcare professional.
How to prevent high cholesterol?
Certain lifestyle changes can help to prevent high cholesterol, also known as hyperlipidemia. Here are some ways to prevent high cholesterol:
- Keep a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can cause your cholesterol levels to rise. Maintaining a healthy weight through a well-balanced diet and regular exercise can assist in lowering your cholesterol
- Eat a healthy diet: A diet high in fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low in saturated and trans fats can help lower
- Regular physical activity: Exercising regularly can help increase HDL (good) cholesterol levels while decreasing LDL (bad) cholesterol levels.
- Limit your alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can raise your triglyceride levels, which can contribute to hyperlipidemia.
- Quit smoking: Smoking lowers HDL cholesterol levels and damages the artery lining, making it easier for cholesterol to build up.
- Control your stress: Chronic stress can raise your cholesterol levels. Stress management activities for hypertension such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can help lower your cholesterol
It’s important to note that changing your lifestyle may not always be enough to lower your cholesterol levels. Medication may be required in some cases to manage hyperlipidemia.
Conclusion
Preventing high cholesterol or hyperlipidemia is essential to maintaining good heart health. Being in shape, eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol intake, and managing stress are all simple lifestyle changes to fight high bp. These daily practices can also help lower your cholesterol levels. However, if you have high cholesterol, it’s crucial to discuss the best course of action with your doctor. Keep in mind that early detection and treatment can effectively protect you from serious health problems. If you’re looking for a physician to help you manage your hyperlipidemia, please go to our find a physician webpage and take your first step towards a healthier tomorrow!
FAQs on Hyperlipidemia
1) What is the symptom of hyperlipidemia?
Hyperlipidemia usually has no discernible symptoms. A blood test is the only way to diagnose hyperlipidemia.
2) What are the 5 signs of high cholesterol?
High cholesterol usually has no visible signs or symptoms. However, some people with hyperlipidemia may develop visible symptoms such as:
- Yellowish patches on the skin
- Yellowish patches around the eyes
- Pain or tightness in the chest
- Hands or feet may develop painful bumps
- Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet
It is important to note that these symptoms are uncommon and may only appear in people with extremely high cholesterol levels. A blood test is the only way to diagnose high cholesterol, which is recommended for adults aged 20 and up every four to six years.
3) Can stress raise cholesterol?
Yes, chronic stress can cause an increase in cholesterol levels. When you are stressed, your body produces hormones that raise your heart rate and blood pressure, which can eventually raise your cholesterol levels.
4) What is dangerously high cholesterol?
Total cholesterol levels greater than 240 mg/dL are considered high and may increase the risk of heart disease. Levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol above 160 mg/dL are also considered high and may increase the risk of heart disease.
5) Can you recover from high cholesterol?
Yes, you can recover from high cholesterol. Making lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and reducing stress can all help lower your cholesterol levels. In some cases, medication may be required to treat high cholesterol. Working with your doctor to develop a personalised treatment plan for high cholesterol is critical.
Disclaimer
The information contained in this article is to educate, spread awareness in relation to hypertension and other diseases to the public at large. The contents of this article are created and developed by BPinControl.in through its authors, which has necessary, authorisations, license, approvals, permits etc to allow usage of this articles on The Website. The views and opinions expressed in this article are views, opinions of the respective authors and are independently endorsed by doctors. Although great care has been taken in compiling and checking the information in this article, The Website shall not be responsible, or in any way liable for any errors, omissions or inaccuracies in this article whether arising from negligence or otherwise, or for any consequences arising therefrom. The content of this article is not a substitute for any medical advice. The Website shall not be held responsible or liable for any consequence arising out of reliance on the information provided in the article.