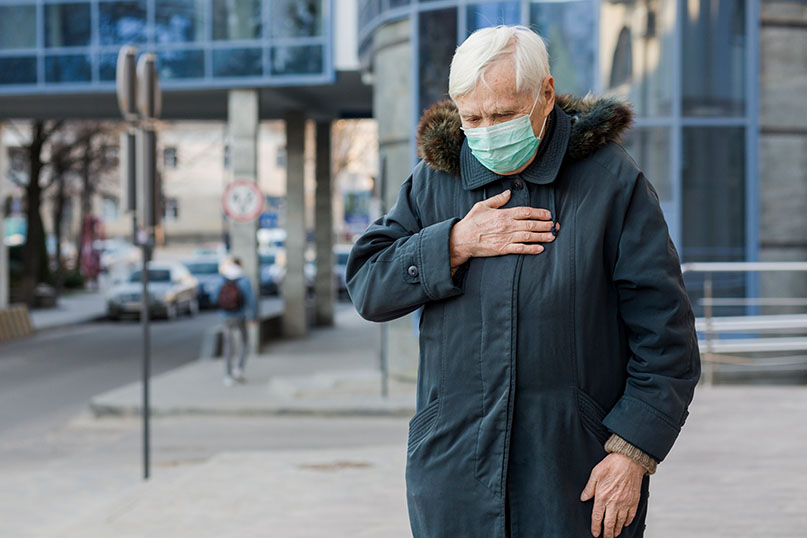
Air pollution comes from natural or manmade pollutants. Factory and automobile emissions also increase this problem. Air pollution can worsen both heart and lung diseases. All heart and artery issues are known as cardiovascular diseases. Some significant causes of this problem include high cholesterol and high blood pressure. Air pollution increases heart attacks as well in many cases. Stress, inflammation, and vascular failure from pollutants can lower heart function and raise cardiovascular risk.
Cardiovascular Disease: Causes and Risk Factors
Cardiovascular disease prevention requires understanding the causes and risk factors of air pollution and heart diseases.
Causes –
- Lifestyle: Having an unhealthy lifestyle, a sleep cycle, and unhealthy meals adds to the problem.
- Blood Pressure: Hypertension is a condition that troubles blood vessels and heart function.
- Hormonal: Genetics has an impact on our heart health.
Risk Factors: –
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking makes the functioning of both the heart and lungs weak.
- Junk Food: Overeating fat, cholesterol, and sodium harms junk food.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of exercise causes most cardiovascular disease.
Hence, to prevent heart disease, learn the causes and risk factors of air pollution and cardiovascular disease.
Link Between Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Disease
Heart disease is worsened by air pollution. Particulates and other contaminants infiltrate the cardiovascular system, causing inflammation, stress, and malfunction that connects air pollution and cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis (accumulation of cholesterol fats in arteries), heart attacks, and strokes are often increased as one spends a long time exposed to air pollution. Through targeted prevention and public health actions, air quality programs can help combat cardiovascular disease. Hence, it is essential to understand ‘how can pollution cause high blood pressure’ to minimise the problem.
Health Impacts of Air Pollution on the Cardiovascular System
The elderly, as well as those with other cardiovascular diseases, may be at risk. Keeping cardiovascular health in check and lowering the economic burden of associated diseases on people is essential, and hence, public health systems need to minimise air pollution through environmental policy. Adopting a better and healthier lifestyle is also crucial for solving the problem of the link between air pollution and cardiovascular disease.
Personal Prevention Strategies
Cardiovascular risk reduction depends on personal prevention. Proactive actions protect heart health and improve well-being.
- Exercise Regularly: Aerobics increase heart fitness.
- Eating Balanced Meal: You can ensure heart health by eating plenty of these foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Avoid Smoking: Give up smoking to decrease the likelihood of heart disease.
These steps and preventive strategies help in achieving better heart health.
Conclusion
Pollution impacts your cardiovascular health, strengthening the call for environmental problems to be tackled. Long-term air pollution exposure worsens the issue of inflammation, oxidative stress, and vascular dysfunction that may lead to air pollution heart disease. The linkage between air pollution, cardiovascular disease, and stroke shows the urgency for a complete reduction of pollution. Environmental laws, sustainable practices, and air pollution awareness are needed to protect cardiovascular health and the environment.
BP in Control’s online portal, Find a Physician, offers a valuable resource to connect individuals with experts specialising in cardiovascular health. This platform helps users locate healthcare professionals who can provide guidance on managing blood pressure and cardiovascular concerns. With the support of these specialists, individuals can access personalised advice to control their blood pressure better and enhance overall heart health.
Disclaimer
The information contained in this article is to educate, spread awareness in relation to hypertension and other diseases to the public at large. The contents of this article are created and developed by BPinControl.in through its authors, which has necessary, authorisations, license, approvals, permits etc to allow usage of this articles on The Website. The views and opinions expressed in this article are views, opinions of the respective authors and are independently endorsed by doctors. Although great care has been taken in compiling and checking the information in this article, The Website shall not be responsible, or in any way liable for any errors, omissions or inaccuracies in this article whether arising from negligence or otherwise, or for any consequences arising therefrom. The content of this article is not a substitute for any medical advice. The Website shall not be held responsible or liable for any consequence arising out of reliance on the information provided in the article.