Hypercholesterolemia: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, & Treatment
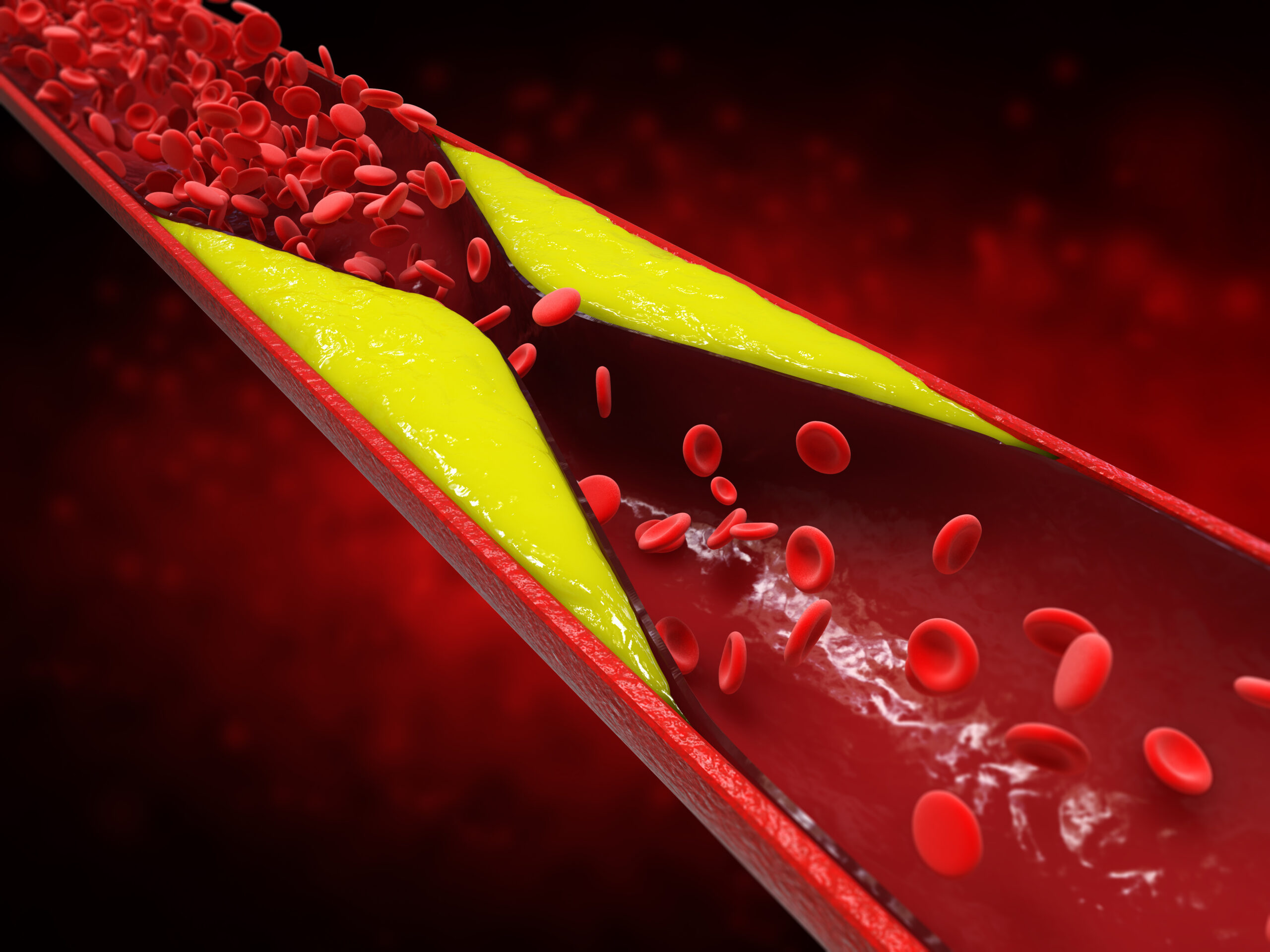
Table of Contents
In the world of health, few terms hold as much weight as “hypercholesterolemia.” While it may appear intricate, its significance is far from obscure. This condition, with a global reach, demands our focus because grasping its intricacies can greatly influence our overall well-being.
This article will help you decode the term — hypercholesterolemia, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and the treatment options that can help you in taking necessary actions beforehand.
What is hypercholesterolemia?
Let’s start with the basics — understanding the meaning of Hypercholesterolemia.
Hypercholesterolemia, often colloquially referred to as high cholesterol, is a medical condition marked by abnormally elevated cholesterol levels circulating in the bloodstream. Cholesterol, a waxy, fat-like substance, is a fundamental component of cell membranes and plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. It functions as a structural component of cell membranes, aids in the breakdown of dietary lipids, and helps produce important hormones (estrogen and testosterone).
Cholesterol itself does not dissolve in the blood, as it is a fatty molecule, and therefore, it needs to be transported through the bloodstream by carrier molecules called lipoproteins. These lipoproteins come in two primary types: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
Some facts about hypercholesterolemia:
- 1 out of every 3 adults has High cholesterol
- It can be genetic or acquired
- High cholesterol levels are a major risk factor for heart disease
- It often goes unnoticed until complications arise
- Sweating can help raise your good cholesterol levels
Hypercholesterolemia — Symptoms
Hypercholesterolemia is a stealthy condition, often lurking in the shadows without noticeable symptoms. Here are some common symptoms to be on the lookout for:
- Xanthomas (fatty deposits that can develop under the skin, typically around the eyes, elbows, knees, or hands)
- Corneal arcus (white or grayish ring that can form around the cornea of the eye)
- Tendon (the deposits of cholesterol can thicken the Achilles Tendon)
Hypercholesterolemia — Causes
- Genetics: Familial hypercholesterolemia is a hereditary condition that leads to exceptionally high cholesterol levels. If a close family member has it, you can be at a higher risk.
- Unhealthy Diet: Consuming excessive saturated and trans fats, often found in processed foods, can elevate cholesterol levels. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help maintain healthy levels.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Leading a sedentary lifestyle can contribute to high cholesterol. Regular exercise can help lower cholesterol levels and improve overall cardiovascular health.
- Obesity: Carrying excess weight, especially around the abdominal area, is associated with higher cholesterol levels
- Diabetes and Hypertension: Individuals with diabetes and hypertension are more prone to hypercholesterolemia, as these conditions can disrupt the body’s cholesterol balance.
- Hypertension Drugs: Additionally, some drugs used to treat hypertension, like thiazide diuretics, can also lead to elevated cholesterol levels as a side effect.
Now, let’s address an important question: who does hypercholesterolemia affect?
Who does hypercholesterolemia affect?
Hypercholesterolemia doesn’t discriminate based on age, gender, or ethnicity. It can affect anyone, from children to the elderly, regardless of their background. However, certain risk factors, such as family history and lifestyle choices, can increase the likelihood of developing this condition. Also, the people who are above 40 years of age are most commonly affected by hypercholesterolemia.
To determine whether you have hypercholesterolemia and to manage it effectively, you need a proper diagnosis.
Diagnosis for Hypercholesterolemia
- Cholesterol Blood Test: A simple blood test, known as a lipid panel, measures your cholesterol levels. This test provides crucial information about your total cholesterol, LDL (low-density lipoprotein), HDL (high-density lipoprotein), and triglyceride levels.
- Family History Assessment: Your healthcare provider will inquire about your family history to determine if there’s a genetic predisposition to hypercholesterolemia.
- Physical Examination: Xanthomas or other physical signs can also be noted during a physical examination.
Treatment for Hypercholesterolemia
The treatment approach for hypercholesterolemia aims to lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications. Here’s how it can be achieved:
- Lifestyle Modifications
- Dietary Changes: Adopting a heart-healthy diet low in saturated and trans fats while increasing fiber intake can make a significant difference.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity on a regular basis helps improve cholesterol profiles and overall cardiovascular health.
- Weight Management: If overweight or obese, losing excess weight can have a positive impact on cholesterol levels.
- Medications
- Statins: These medications are often prescribed to lower LDL cholesterol levels. Common statins include atorvastatin and simvastatin.
- Other Medications: In some cases, additional medications like bile acid sequestrants or PCSK9 inhibitors may be used in combination with statins.
- Genetic Counseling: For individuals with familial hypercholesterolemia, genetic counseling may be recommended to understand the inheritance pattern and assess the risk to family members.
- Regular Monitoring: Routine cholesterol checks are essential to track progress and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Summing Up
Hypercholesterolemia serves as a reminder that our health is a precious asset that requires our attention and care. It’s a condition that knows no boundaries, affecting individuals from all walks of life. Whether young or old, regardless of gender or background, anyone can find themselves grappling with the challenges posed by high cholesterol.
It is paramount to recognize that hypercholesterolemia is not a standalone issue; rather, it is a critical piece in the intricate puzzle of cardiovascular health. By seeking timely medical guidance and adopting healthy lifestyle choices, we can take proactive measures to manage this condition and safeguard our hearts.
And before we conclude, for more information on hypercholesterolemia and related topics, be sure to check BPinControl’s website. With the Find a Physician portal, you can easily access the best doctors in your area. Additionally, you can also look for the blogs that the website offers which includes many health-related subjects.
FAQs
1. Is hypercholesterolemia LDL or HDL?
Hypercholesterolemia primarily refers to high levels of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol in the blood. LDL cholesterol is often referred to as “bad” cholesterol because high levels of it can increase the risk of heart disease.
2. What are the 5 signs of high cholesterol?
The five signs of high cholesterol may include:
- a) Chest pain or angina
- b) Yellowish deposits of cholesterol around the eyes (xanthomas)
- c) Xanthelasma, which are fatty deposits on the eyelids
- d) High Blood Pressure
- e) Extreme Fatigue
3. Can hypercholesterolemia be cured?
Hypercholesterolemia cannot typically be “cured” in the traditional sense, but it can be managed and controlled through lifestyle changes and, if necessary, medication. Lifestyle modifications include adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Medications, such as statins, may be prescribed by a healthcare provider to help lower cholesterol levels when lifestyle changes alone are insufficient.
4. Is 250 cholesterol high?
A total cholesterol level of 250 mg/dL is considered high. However, it’s important to note that cholesterol levels should be interpreted in the context of individual risk factors and overall cardiovascular health. Your healthcare provider will assess your cholesterol levels along with other factors to determine your risk and recommend appropriate treatment or lifestyle changes.
5. Which statin is best for hypercholesterolemia?
The choice of the best statin for hypercholesterolemia depends on various factors, including your individual health profile, any other medications you may be taking, and your tolerance for potential side effects. Commonly prescribed statins include atorvastatin (Lipitor), simvastatin (Zocor), rosuvastatin (Crestor), and pravastatin (Pravachol), among others. Your healthcare provider will evaluate your specific situation and prescribe the statin that is most appropriate for you. They will also monitor your cholesterol levels and adjust your treatment as needed.
Disclaimer
The information contained in this article is to educate, spread awareness in relation to hypertension and other diseases to the public at large. The contents of this article are created and developed by BPinControl.in through its authors, which has necessary, authorisations, license, approvals, permits etc to allow usage of this articles on The Website. The views and opinions expressed in this article are views, opinions of the respective authors and are independently endorsed by doctors. Although great care has been taken in compiling and checking the information in this article, The Website shall not be responsible, or in any way liable for any errors, omissions or inaccuracies in this article whether arising from negligence or otherwise, or for any consequences arising therefrom. The content of this article is not a substitute for any medical advice. The Website shall not be held responsible or liable for any consequence arising out of reliance on the information provided in the article.


Comments (0)
No comments found.Add your comment